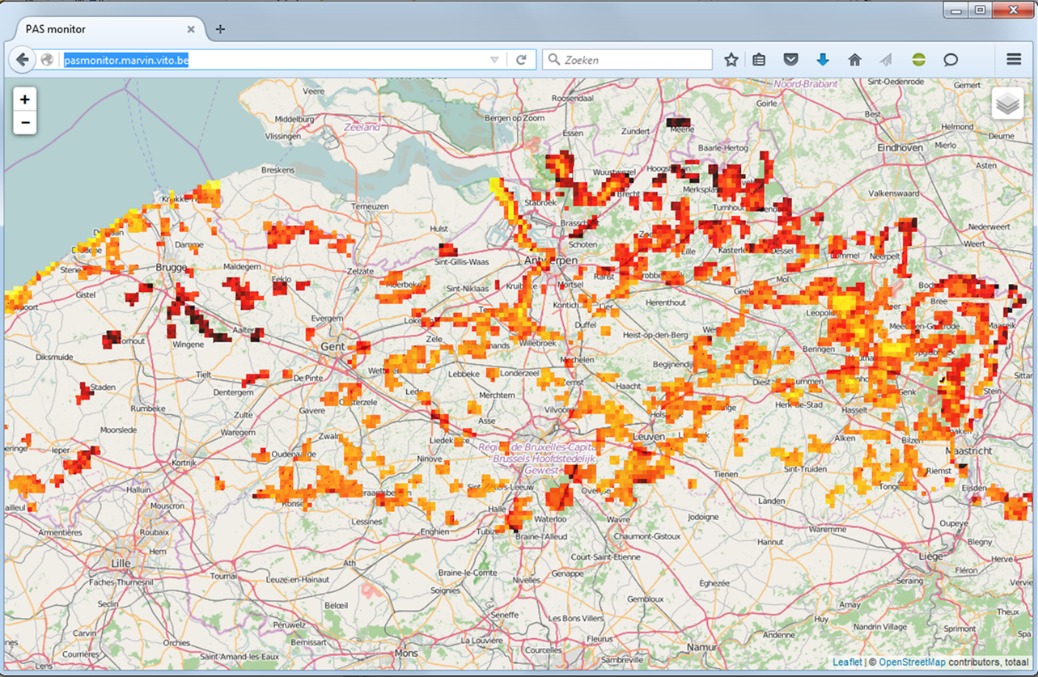
Atmospheric deposition of reactive nitrogen is a major threat to biodiversity in Europe. Critical loads for the protection of habitats from nitrogen deposition are being exceeded across large areas of Europe, including Flanders.
The Habitats Directive obliges EU member states to set conservation objectives for Special Areas of Conservation (SACs) and to establish the necessary conservation measures. In Flanders a high percentage of these SAC areas have nitrogen deposition exceeding the Critical loads. The key sources for nitrogen deposition in Flanders are: ammonia from livestock housing, nitrogen oxides from road traffic and industrial installations.
In order to decide on what mitigation measures are required to reduce the impact of nitrogen deposition on the SACs, modelling at both regional and local scale is required. This requires complex modelling and coupling of regional and local scale models to capture absolute levels of nitrogen deposition from all (European) emission sources as well as the detailed local nitrogen deposition from ammonia and nitrogen oxides in the vicinity of sources.
Policy makers requested software tools built around the modelling results to:
- Show them where and what the key nitrogen sources are;
- Allow them to explore options for most effective/efficient abatement strategies at regional level (generic versus specific policies);
- Decide whether a permit to livestock owners can be granted based on the impact of their (new) activities on the ecosystems.
In close collaboration between the client, our air quality experts and IT experts two IT solutions have been developed to answer these request.
- Web application for the policymakers to analysis nitrogen eutrophication in Flanders;
- Web application to assess the impact of livestock farming on the nitrogen deposition to control livestock permits.
Web application to analyse nitrogen eutrophication in Flanders